Thoracic osteochondrosis is rare in clinical practice. Previously, it was diagnosed mainly in the elderly, but now it is often detected in patients under 35 years of age. More often, the condition develops in women than in men. This degenerative dystrophic disease is difficult to diagnose, since severe symptoms appear only in the later stages.
In addition, the symptoms of this disease can easily be confused with signs of pulmonary and heart failure. This disease cannot be left untreated, as it can cause curvature of the spine, development of persistent pain syndrome and other complications that can negatively affect the quality of human life.
What is thoracic osteochondrosis?
In the international classification of diseases, this pathology has an ICD-10 code - M42. Thoracic osteochondrosis is much less common than cervical or sacral. This is no coincidence. Due to the presence of a rigid rib cage in that part of the body, that part of the spine is less physiologically mobile.
The thoracic region contains more vertebrae than cervical and lumbar, but in this part of the spine the discs are thinner. These anatomical characteristics contribute to the decrease in mobility of this part of the spine, making it less subject to injuries.
However, when exposed to a number of adverse factors, osteochondrosis can develop. At first, there are signs of damage to a disc, but in the future, other elements may be involved in the pathological process. As the disease progresses, bone elements are damaged, as well as the ligaments and muscles that support the spine.
Degenerative dystrophic processes in the thoracic region grow more slowly. Often, years pass before the fibrous rings of the damaged discs are destroyed so much that protrusions and hernias appear.
Serious clinical manifestations occur after a critical decrease in the height of the discs and the entrapment of the roots. This can lead not only to the back, that is, attacks of short duration pain in the thoracic region, but also to the violation of the innervation of Organs internal organs. It is much more difficult to treat compressed nerve roots that extend into this area.
Reasons for development
In most cases, spine problems do not appear suddenly. A disease like osteochondrosis is no exception in this regard. This pathology, which affects the intervertebral discs, is the result of long-lasting degenerative-dystrophic processes. In most cases, it is impossible to determine exactly what triggered the development of the disorder. Factors that can cause the appearance of osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine include:
- congenital or acquired deformities of the spine;
- overweight;
- spine overload during pregnancy;
- infectious diseases; hypothermia;
- metabolic disorders;
- hormonal disorders;
- chronic stress;
- bad habits;
- connective tissue diseases;
- dysplastic changes;
- posture disorders;
- unhealthy diet;
- injuries.
Detraining negatively affects the condition of the spine. People who lead a sedentary lifestyle are more likely to suffer from thoracic osteochondrosis. In addition, age-related changes and slowing metabolism, seen in patients over 55 years of age, contribute to the appearance of these disorders.
Genetic predisposition can be a factor that can provoke the development of pathologies. The genes that create the conditions for the onset of breast osteochondrosis have not yet been identified, but in people with a family history of cases of this disease, it is diagnosed more often.
Symptoms and signs
The clinic of this pathological condition depends on the neglect stage of the process, the level at which the intervertebral disc injury occurred and the patient's age. In the early stages of development, there are no specific signs, but general symptoms can occur periodically. Often, in the early stages of development, the disease manifests itself only with the onset of cold weather or after excessive physical effort. Initial manifestations of the development of osteochondrosis of the thoracic region include:
- rapid fatigability;
- back pain and pressure;
- muscle spasms;
- cold ends.
As the disease progresses, the patient's condition worsens. Chest pains appear. They occur frequently especially in the context of prolonged stay in one position or with sudden movements. In addition, severe pain syndrome can appear when lifting weights. Rotating the torso can cause increased pain. The presence of osteochondrosis is also indicated by the occurrence of uncomfortable pain in the region of the shoulder blades.
Often, osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is accompanied by the appearance of an abnormal curvature. In severe cases, the patient may develop a lump. In addition, this disease can cause pain to appear during deep breathing and exhalation.
When the nerve roots are compressed, a sensation of numbness usually occurs in the upper limbs and the skin of the upper body. Due to the violation of innervation and blood circulation, a skin prickling sensation appears. The feet and hands are always cold. Limb sensitivity may be present. In advanced cases, this disease can lead to symptoms of damage to other organs due to the violation of its innervation. In the last stages of the process, it is possible that:
- intercostal neuralgia;
- fecal disorders;
- swelling;
- heartburn and nausea;
- itching and burning in the feet;
- violations of the reproductive system;
- asthma attacks.
As the pathology progresses, a person's ability to work decreases. Physical activity is minimized. In the future, this disorder may create preconditions for the development of serious complications. The risk of pathological fractures increases. The curvature of the spine leads to compression of the organs located in the chest.
With an unfavorable course, the disease continues with violation of the heart muscle and decreased lung volume. Most of the time, these serious complications are accompanied by generalized osteochondrosis, in which several intervertebral discs are affected at the same time.
Degrees of thoracic osteochondrosis
The existing classification subdivides the process of developing this pathological condition into 4 degrees. Each of them is characterized by the presence of a series of changes in the structure of the intervertebral discs, vertebrae and other elements that make up this part of the spine.
First degree
In the first degree of pathology, there are no pronounced clinical manifestations, but specific changes in the structure of the intervertebral discs can already be revealed with a comprehensive diagnosis. The fibrous ring, which receives less moisture and nutrients, gradually loses its elasticity. Microfissures are often formed in tissues, in which the pulposus nucleus is compressed. The displacement of the discs to the vertebral canal is possible. Overhangs are formed. There are no signs of rupture of the fibrous ring.
High school
With the transition from the disease to the second degree, the first clinical manifestations are observed. Patients occasionally experience pain and other neurological signs. When making a specific diagnosis, signs of decreased elasticity of the tissues that form the fibrous ring can be detected. Cartilage becomes very thin, which increases the risk of hernias. There is a decrease in the height of the intervertebral discs, due to which the structures of the spine acquire abnormal mobility.
Third grade
In the third stage, changes in the structure of the discs become so pronounced that the first signs of kyphosis or scoliosis appear. Often, at this stage of the process, the damaged fibrous ring breaks. This phenomenon is accompanied by the exit of the pulposus nucleus beyond the disc. A hernia in formation, depending on the direction of the protrusion, can compress the nerve roots or the spinal cord. Severe pain and neurological disorders occur. Spine mobility increases, which creates conditions for injuries and fractures.
Fourth grade
With the transition from pathology to the fourth degree of development, the structure of the intervertebral discs is so disturbed that they stop performing the amortization function. The fibrous ring and pulpous nucleus lose elasticity. These elements begin to ossify. For violation of the disc's amortization function, the vertebrae suffer, which support a lot of load.
At the edges of the vertebrae adjacent to the damaged disc, osteophytes, that is, bone growth, begin to grow rapidly. The surrounding ligaments are involved in the pathological process. They lose elasticity and fail to support the spine properly. In addition, at this stage of the development of the pathological process, the work of the muscular system is interrupted.
Making a diagnosis
When signs of development of this disorder appear, the patient needs an appointment with a neurologist and an orthopedic surgeon. First, the doctor does an external exam and collects an anamnesis. Laboratory tests frequently prescribed in the diagnosis of this disease include blood and urine tests. To obtain information about the presence of defects in the structure of the spine, an X-ray is taken. This research reveals:
- decreasing the height of the disk;
- cut-out edges of elements;
- hernia;
- alteration of the vertebral bodies;
- forming osteophytes and so on.
To clarify the defects in the disc structure, a discography is designated. This study makes it possible to identify the irregular contours of the pulpous nucleus, assess the degree of disk destruction and decrease the tissue density. CT and MRI scans are usually done for better visualization. Considering that the clinical manifestations of thoracic osteochondrosis are similar to the symptoms of ischemic heart disease, electrocardiography is often prescribed to differentiate these conditions.
Treatment options
This pathological condition requires complex treatment. First, patients are selected medications that help to eliminate symptomatic manifestations and improve the nutrition of intervertebral discs. Medication should be supplemented with physical therapy and exercise therapy. As a supplement, you can use some folk remedies. In addition, it is recommended to follow a specific diet.
Medicines
In case of severe pain syndrome, the patient is advised to remain at rest in bed. This will reduce the intensity of the pain. To eliminate discomfort, pain killers and NSAIDs are often prescribed. If the pain syndrome manifests very intensely, blockages may be necessary. Often, glucocorticosteroids are prescribed to eliminate pain in this disease.
Chondroprotectors are prescribed to improve the saturation of nutrients and water in the intervertebral discs. In some cases, antispasmodics and muscle relaxants are prescribed in short courses. These medications help to relieve muscle spasm. If necessary, diuretics are prescribed to eliminate soft tissue edema. To improve the condition of the nerve endings submitted to compression, the patient needs B vitamins.
Physiotherapy and massage
Therapeutic exercises and massages are the most important components of osteochondrosis treatment, but they can only be used after suppression of symptoms with medications. Properly selected exercises help improve lung ventilation and strengthen the muscle corset that supports the spine.
First, all necessary exercises must be learned under the supervision of an exercise therapy instructor. In the future, the patient will be able to exercise at home. People with this condition may be advised to take classes at the pool.
Massage helps to eliminate muscle hypertonia and improve soft tissue nutrition. In order for the procedures not to cause damage, they must be performed by a specialist. In most cases, a classic massage is carried out, which involves successively rubbing, smoothing and pinching the problem area. Acupressure and segmental massage can be of great benefit. These techniques involve impacting pain points. They help to improve blood circulation and lymphatic drainage. In most cases, it is enough for patients to do the procedures 2 to 3 times a week.
Acupuncture
This method involves placing needles in areas of the patient's body. This method allows you to quickly eliminate muscle spasms and pain. Acupuncture procedures must be performed by a professional in the field. If a specialist does this, the procedure will be almost painless. Acupuncture is contraindicated for people who suffer from oncological diseases, mental disorders. The use of this method of treating osteochondrosis in the presence of severe inflammatory processes is not recommended.
Manual therapy
Manual therapy helps to restore the correct anatomical position of the vertebrae. In addition, this method helps to reduce the intensity of pain and muscle spasms. This effect helps to restore the ligamentous apparatus. These procedures can delay the development of this pathological condition. The duration of the manual therapy course is selected individually for the patient.
Post-isometric relaxation technique
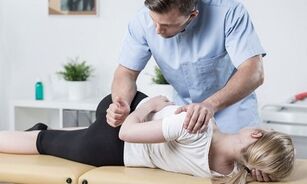
Post-isometric relaxation is a special technique that involves contracting all the muscles around the spine and then relaxing them.
These exercises should be performed under the supervision of a specialist who can assess the accuracy of the movement and the intensity of muscle tension. This method allows you to quickly eliminate the pain and restore the normal function of the muscles and ligaments.
Folk remedies
It is impossible to treat osteochondrosis with folk remedies alone, as this approach can aggravate the course of the disease. It is best to use various herbal formulations and other natural ingredients as a complement to traditional therapies. You should get a doctor's recommendation on the convenience of using this or that folk remedy before you start using it.
Celery root
Properly cooked celery root is believed to help saturate cartilage tissue with nutrients and water. To prepare this product, 1 root must be well chopped and pour 1 liter of boiling water. You need to insist on writing for at least 8 hours. After this time, it is necessary to strain the product and take 1 teaspoon. 3 times a day before meals.
Sunflower root
For the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, it is customary to use a sunflower root decoction. To prepare this product, you will need about 1 cup of chopped vegetable ingredient, pour 3 liters of water. The mixture should be boiled for 3-5 minutes. After that, the agent must be cooled and taken in the form of tea for several days. To improve the drink's flavor, honey can be added. It is preferable to store the rest of the medicine in a thermos.
Ointment for home
A simple, homemade ointment can be used to scrub osteochondrosis. To prepare this product, it is necessary to melt about 150 g of lard in a water bath. After that, 2 tablespoons should be inserted into it. I. natural wax.
The composition must be boiled for at least 20 minutes. After that, 1 tablespoon should be added to the heated mixture. I. fir oil. The product should be boiled for another 20 minutes. Last but not least, 2-3 minutes before removing the container from the heat, 1 tablespoon is introduced into the mixture. I. ammonia. The finished composition must be distributed in pots. Store the homemade ointment in the refrigerator.
Nutrition for thoracic osteochondrosis
Patients suffering from osteochondrosis of the thoracic region need a balanced diet. A sufficient amount of protein-rich foods should be introduced into the diet. It is advisable to regularly consume dishes that contain large amounts of chondroitin, including fish gelatin, frozen meat and so on. It is imperative to introduce fermented dairy products, vegetables and fruits to the diet. The dishes must be steamed or roasted. Fatty and fried foods should be avoided. It is advisable to eat in small portions, but often. This will avoid overeating.
Aggravation: what to do?
In the acute period of the disease, it is desirable to reduce activity to a minimum. If possible, you should avoid postures in which the pain syndrome increases. First aid for exacerbating osteochondrosis involves the use of medications that reduce the severity of edema, inflammation and pain. The patient is advised to rest in bed. It is advisable to follow a moderate diet during this period. Only after eliminating the symptoms can you start exercise therapy and physical therapy.
Forecasting
Now, this disease can be cured only in the early stages of development. With late diagnosis, therapy aims to eliminate symptoms and improve spinal mobility. In some cases, surgical treatment is required. With an integrated approach to therapy, a person suffering from this pathology can lead a complete lifestyle without experiencing pain and other neurological disorders.
Prevention
To prevent the development of this pathological condition, it is recommended to avoid sudden weight lifting. You should always dress for the weather, avoiding hypothermia. In addition, to prevent osteochondrosis, one must combat hypodynamics and monitor posture. As part of the prevention of this pathology, correct nutrition and careful weight monitoring are recommended.

























