It is rarely possible to diagnose thoracic spine (OG) osteochondrosis, unlike cervical and lumbar osteochondrosis, which occur in every 2-3 patients aged 18 years and over. This phenomenon is explained by the special structure of the thoracic part - the presence of a greater number of discs, which in turn have a finer structure. This part of the spine has low mobility and therefore the load on it is not high, as the main "blow" is carried by the sternum along with the ribs.
The main reason for the onset of development of thoracic pathology is an increased load on the intervertebral discs and, as a result, a violation of metabolic processes as well as their structure.. . . In the presence of such a disease, the shock-absorbing properties of the disc are lost, the fibrous ring becomes thinner, dry, after this process, the nerve endings become inflamed, the person experiences constant pain, discomfort, and motor activity decreases. . With the rapid course of the disease, it affects the spinal ligaments and joints.
Now, many experts consider the rule of classifying osteochondrosis not by course stages but by degrees, which are also differentiated by the peculiarities of the symptoms.
If we take into account the general symptomatology, then osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is not as pronounced, unlike the other types, however, there is a characteristic clinical picture. Thus, the patient may complain about the presence of the following signs:
- pain in the chest region, often aggravated by prolonged exposure to a position or at night;
- painful sensation between the shoulder blades, while it increases with arm elevation or after physical exertion;
- discomfort, pain when trying to breathe deeply, this symptom is also noticed on exhaling;
- when walking, there is pain in the ribs and a tight feeling in the chest area.
These manifestations can accompany the person for several weeks, which should be considered an exacerbation of the disease.
What other symptoms can be seen with HO? In addition to the main clinical picture, in some cases the following manifestations are possible:
- numbness in the upper extremities, "shivering" sensation running through the skin;
- disturbance of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract;
- feeling cold in the legs, the inability to warm them.
In addition, the characteristic signs of this disease are the back - the occurrence of acute pain between the shoulder blades and back pain - a slow pain syndrome that does not have a pronounced picture.
It should be noted that, like any other type of osteochondrosis, chest disease often affects people with an inactive lifestyle. Sitting in front of the computer, leaning over, heavy physical exertion, also become a triggering factor in the development of the disease.
How the disease manifests in women and men
The development of degenerative dystrophic processes in the thoracic region in patients is considered a diagnosis - thoracic osteochondrosis. With this disease, there is destruction of the intervertebral discs and malnutrition in the structures of the connective tissue. Also, the blood circulation process is disrupted as the chest area becomes inactive. And the pain syndrome itself occurs due to pinching of nerve endings during the progression of the pathology.
As statistical data indicate, HO is diagnosed in women sometimes more often than in men and, at the same time, at a younger age. The main reason for this phenomenon is the change in hormone levels when entering menopause. The impetus for the development of the disease is also osteoporosis, which is often detected in women during the onset of menopause.
Therapeutic measures are developed taking into account the clinical picture of the pathology. Severe symptoms do not appear immediately; it often takes a long time to suspect the presence of the disease. Specifically, it is possible to establish a diagnosis already in the course of a pronounced condition, when symptoms become evident. When it comes to a pronounced period, two types of symptoms must be distinguished here:
- Development of painful sensations. . . We are talking here about the occurrence of pain in the thoracic region, between the shoulder blades, radiating to the solar plexus region. The pain syndrome can migrate to the neck area, simulating cervical osteochondrosis and to the arm. Often, women notice pain in the mammary glands, mistaking them for breast pathologies. As a rule, the sensations of pain are not permanent, they are painful, but at the same time, they are not intense.
- blood pressure disorder. . . In breast osteochondrosis in women, there is the hypertensive syndrome, which is characterized by increased pressure and can cause a hypertensive crisis. A distinguishing feature of normal hypertension may be the presence of a minimal effect from the use of medications that lower blood pressure. If you have already been through similar situations, you should also see a vertebrologist.
In addition to the above, other signs of degenerative dystrophic disorders in the thoracic spine should be distinguished:
- Pain in the left side of the thoracic region,not associated with heart damage. . . In medical terminology, this phenomenon is called cardialgia. It is not difficult to diagnose it, as, with the development of such a symptom, it cannot be stopped by the use of cardiac drugs.
- Disturbance in the functioning of the digestive system. . . Often, as osteochondrosis begins to progress, problems start in Organs internal organs, most often in the gastrointestinal tract. The most striking example is the formation of heartburn, an increase in acidity and a feeling of constant bloating (flatulence). Among other things, there can be problems with the digestion of food - nausea after eating, heaviness, bloating. In the context of all this, chair work is also interrupted - frequent constipation or diarrhea.
- respiratory disorders. . . As the dystrophic process occurs in the chest region, cases of violation of the respiratory system are not uncommon. All of this is accompanied by irrational dizziness, general weakness, shortness of breath and other signs that may indirectly resemble cardiac pathology or pressure problems (arterial/intracranial).
As far as therapy is concerned, it depends a lot on the signs of the pathological process. To relieve pain, pain relievers are prescribed, including NSAIDs in the form of ointments or gels. During the exacerbation period, muscle relaxants are more effective, reduce smooth muscle spasm, relax muscles, relieve pain syndrome, evaluations of their use are positive. When the pain becomes completely unbearable, analgesic blockade is used.
thoracic treatment
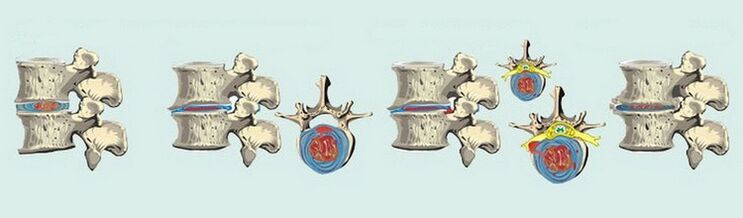
Exactly how GO will manifest itself depends on the pathological changes that occur in the intervertebral discs. It is common to distinguish four stages of the course of degenerative dystrophic disorders in the chest:
- The first. . . The symptoms are not particularly pronounced, however the process of dehydration of the discs in the thoracic spine has already started. As a result, they lose their elasticity, acquire a flatter appearance, but at the same time they can still support certain loads. Occasionally, sore-type painful sensations are disturbed but not mild and often do not require the use of pain relievers.
- The second. . . At this stage, the negative changes affected the fibrous ring, there are several types of damage - cracks, loss of stability. There are changes in the pain syndrome, it becomes more intrusive, palpable, intensifies with increased motor activity - curves, turns.
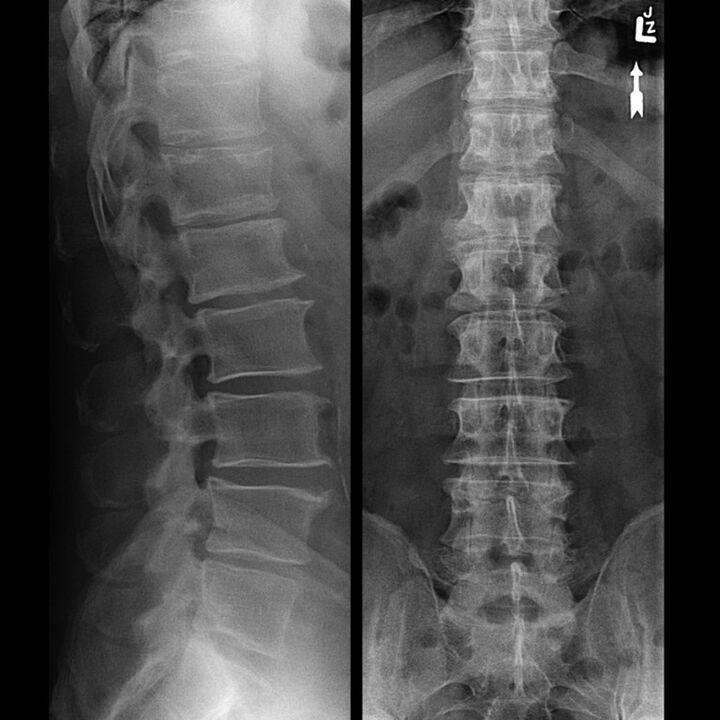
- The third. . . On x-rays, the fibrous annulus rupture is clearly visible and a hernia begins to form. The sensations of pain become clearer, from a whining character can flow into a sharper one, intensifying with movement and even at rest.
- bedroom. . . Spondyloarthrosis is actively developing, in a context of convergence of vertebrae and erasure of discs. As a result, the connective tissue of the fibrous ring is replaced by bone tissue, which significantly limits motor ability.
The clinical picture of thoracic osteochondrosis is such that the diagnosis of this disorder is more likely:
- Ache. . . Its location is almost always in a specific place, usually on the left. After a while, it spreads all over the chest area, breathing becomes difficult, climbing stairs or exercising becomes difficult.
- increased pain. . . Strengthening occurs when turning or leaning, in general, with any physical activity, the same is observed when trying to breathe deeply.
- muscle spasm. . . Muscle spasm is added to the above symptoms, the contraction falls mainly in the upper back. In rarer cases, this symptom is present in the lower back.
Separately, it is important to look at intercostal neuralgia, which tends to last for several weeks and then disappear on its own. During this time, the person is accompanied by chest discomfort, aggravated by movement, discomfort when trying to inhale/exhale deeply. Women may have the impression that they have problems with their mammary glands, which will make them think about treating them and, for men, the sensation of a foreign object behind the breastbone.
It should also be noted that the entire clinical picture described above intensifies at night or after hypothermia. The next morning, as a rule, is easier, but at nightfall everything is repeated.
How to treat, what methods are there, what to take? With regard to therapeutic measures, they should be started as early as possible. Often, in the early stages, it is possible not even to use medication, but only with regular gymnastics - exercise therapy.
The later stages of pathology development, in 2 degrees, involve drug use. This includes several groups of medications, the most popular ones are shown in the table below.
| drug group | The main action of the drug |
|---|---|
| Analgesics, analgesics | They alleviate the pain syndrome, reduce its manifestation. |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) | Eliminate inflammation, relieve pain, swelling. |
| Chondroprotectors | They increase the production of intra-articular secretions, delay the process of cartilage destruction and reduce the manifestation of the inflammatory process. |
| muscle relaxants | They reduce skeletal muscle tone, have a relaxing effect, and help to deal with back pain effectively. |
| sedatives, sedatives | For a more effective therapy, since severe pain can cause stress, which worsens the treatment effect. |
In addition to essential medications, a course of vitamin medications is recommended.
In case of worsening of the entire clinical condition, the main objective of therapy will be the relief of symptoms. For a more pronounced and quick action, pain relievers are prescribed in the form of injections as well as the steroid type.
After eliminating the exacerbation and achieving stability of the state, it is necessary to start basic therapy. A very wide range of medications can be prescribed, as only a complex effect on the disease can give positive results.
The main drugs are described in the table above, below with more details about them. Therefore, the basic treatment will include the indication of such medications:
- Chondroprotectors.They are used in the form of pills and for local therapy, in the form of ointments or gels. It is impossible to exclude the use of such medications, they are the basis for a complete therapy. Its action aims to inhibit the process of destruction of cartilage tissue and subsequent progression of dystrophic changes. Furthermore, they increase the regenerative capacity of cartilage. However, it is impossible to completely get rid of the pathology with the help of such medicine; it should not be considered a panacea.
- Vasodilator. . . They are needed to improve blood circulation and hence nutrition in the affected area. Most of the time, a very effective medication is prescribed that improves the blood microcirculation and helps to deal with the pain that occurs at rest.
- local therapy. . . For the best effect, ointments or gels are prescribed. Thus, good results can only be achieved with the help of a complex effect, therefore, when prescribing NSAIDs and chondroprotectives, it is customary to recommend additional ointments from the same pharmacological groups. Also popular are bee or snake venom creams, they have a pronounced analgesic effect and are a good addition to the main therapy.
- Vitamins. . . In particular, group B vitamins are prescribed. They have analgesic properties, help to deal with inflammatory processes and the violation of nerve endings.
- Without fail, along with the drug effect, a course of physical therapy, massage therapy, exercise therapy is prescribed.
What other methods of therapy should be included in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis? An experienced professional will strongly recommend the following techniques:
- magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, therapeutic mud;
- physiotherapy exercise complex;
- acupuncture, acupressure.
It is also recommended to follow a certain diet, you must exclude the use of alcohol, spicy foods, reduce the use of salt.
Special attention must be given to therapeutic exercises, which must be performed daily, preferably several times a day. Note that the exercise set is individually developed by the treating physician - an orthopedist or traumatologist. Physical education is carried out in the absence of exacerbations, when there is no pronounced pain, in the case of acute pain syndrome, maximum rest must be respected.
Sports with osteochondrosis are not the last thing. With this condition, it is important to regularly perform all prescribed exercises that will strengthen the muscles and positively affect the treatment outcome.
We should also mention traditional medicine. On the Internet you can find many recipes based on natural raw materials. It is not recommended to get carried away by folk remedies as an independent method, due to the fact that their effectiveness will be minimal and, in many cases, zero. However, as an adjunct to conventional therapy, folk remedies may be recommended. The following homemade recipes are known:
- Ingredients for the first one: 3 tablespoons of rye flour, 1 tablespoon of turpentine and 1 teaspoon of iodine and garlic. Mix everything well and use as an ointment at night.
- For the second: 5 tablets of metamizole sodium and 5 ml of camphor alcohol. Bring the tablets to powder state, then pour in the alcohol and apply overnight in the form of applications.
A needle applicator is considered another alternative therapy. Its action aims to reduce the pain syndrome through needle massage.

In the event that all the described methods of therapy did not give the desired result or proved not to last, the question of prescribing an operation is decided. Surgery is necessary when it is not possible to eliminate the painful syndrome, the degenerative-dystrophic process continues to develop, at the same time, there are negative changes in the functioning of internal organs. If the doctor still recommends that you have the operation, you should not refuse immediately. Timely intervention will allow you to get rid of such a problem, fully restore organ function, and rule out the development of complications.
Surgery usually involves two steps. The first is aimed at eliminating the cause - decompression, through which the pain syndrome is eliminated. The second stage is the subsequent stabilization of the spine.
Osteochondrosis of the thoracic region is a serious pathology that can not only impair the functioning of the musculoskeletal system, but also negatively affect systems and organs.
It's important to monitor your own health, take preventative measures, monitor your diet, and be smart about physical activity. Regular exercise is an effective prevention of osteochondrosis, but don't forget that any load should be moderate.
Cervicothoracic-type treatment
Osteochondrosis of the cervicothoracic region is not considered an independent pathology. In this case, we are talking about a set of disorders that appear in the intervertebral discs and are capable of affecting muscle tissue, as well as nearby organs.
Cervicothoracic osteochondrosis is far from being uncommon, as more than 20% of diagnoses are attributed to this disease. The disease is very insidious, the variety of clinical picture in many cases makes the physician suspect of other diseases not related to the spine. For example, a doctor might suggest the presence of angina pectoris, recommend a drug that, in the end, simply won't work, and worst of all, it will negatively affect the state of the cardiac system. For this reason, it is very important to differentiate osteochondrosis from internal organ pathologies. Thus, for dystrophic disorders in the cervicothoracic region, the following signs are characteristic:
- frequent headaches;
- loss of strength, followed by dizziness;
- neck pain, flowing to the shoulders, shoulder blades, a state of muscle stiffness;
- compression of the intercostal nerve roots, hence the pain syndrome, as well as its exacerbation;
- blood pressure violations, there may be drops from hypertension to hypotension, more often in women;
- decreased visual acuity, problems with the hearing aid (hearing loss);
- in men, decreased potency with nerve overload in the context of the disease.
An important point is formulating the correct diagnosis, several diagnostic measures will be needed here, which will include: X-ray examination, ultrasound, MRI, CT scan.
Comprehensive treatment is mandatory and must include:
- medicines;
- various physical therapy techniques;
- physiotherapy;
- non-traditional therapy (acupressure, acupuncture).
It is also important to be careful with non-pharmacological measures, for example: reducing physical activity, which includes minimizing the load, changing the mattress and purchasing an orthopedic pillow.
Atypical symptoms, sensations and pain
In addition to the typical pain that manifests in thoracic osteochondrosis, there are many atypical pains that cannot be associated with spinal diseases. However, you should be aware of them:
- Heartache. . . Often, with such a condition, heart pains appear while mimicking heart attack attacks. A distinguishing feature is its duration. Unlike true heart pain, with osteochondrosis, the pain is prolonged, it can be bothersome for several weeks. Furthermore, the use of traditional medications does not reduce the manifestation of pain. This is where it is worth thinking about the presence of another pathology not related to the heart.
- Imitationpathologies of the mammary glands. . . This clinical picture applies directly to patients. Often, thoracic osteochondrosis brings to mind breast disease, as the woman can observe pain in the chest region for a long time, which spreads to the glands. Identifying the true cause of such a symptom, or at least excluding problems with the mammary glands, is only possible after examination by a mammologist.
- Pain in the abdominal cavity. . . This symptom makes one suspect the presence of gastritis and other diseases of the digestive system. A gastroenterologist may mistakenly diagnose pancreatitis or cholecystitis. It is possible to refute or confirm these diagnoses with the help of a thorough examination.
- In addition to these signs, the patient may experience a pronouncedchest discomfortdescribed as having a foreign object. It is often difficult to breathe or exhale deeply, feeling that it is impossible to breathe deeply, shortness of breath with little physical activity.
The treatment process for degenerative-dystrophic disorders is not easy, it requires a lot of time, patient effort and the assistant physician's qualification.
Be sure to consult your doctor before treating illnesses. This will help to take individual tolerance into account, confirm the diagnosis, make sure the treatment is correct, and rule out negative drug interactions. If you use prescriptions without consulting your physician, it is at your own risk and expense. All information is presented for informational purposes only and is not a medical aid. All responsibility for the application is yours.

























