These two words are quite similar in listening comprehension, so many people who say the words "arthritis" and "arthrosis" don't even suspect that these are completely different diseases, although they are associated with joint problems. In fact, these two diseases are very serious and it is worth knowing what is the difference between arthritis and arthrosis, if only to avoid being in an uncomfortable position in a conversation, because the health theme is one of the "eternal" themes when oneperson communicates with another.
What is arthritis
Arthritis is a condition that affects most people in middle age (under 40), although there may be exceptions. According to statistics, few people suffer from arthritis, no more than 2% of the total population. However, in essence, arthritis is a serious inflammatory process in which joint problems are only the visible part of the widespread inflammation.
In arthritis, the main cause of the disease is hidden much more deeply than the swelling of the joints, as well as the pain that does not leave the patient even during the night rest period (sometimes these pains only intensify). This inflammation can be caused by infection or a malfunction of the immune system. The joints are not the only organs affected by inflammation. Often, a powerful blow strikes a person's internal organs such as the liver, heart and kidneys. If the problem of arthritis is ignored, then it is very dangerous not only for human health, but also for your life.
What is arthrosis
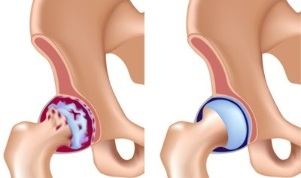
Arthrosis, in general, is a change related to the age that a person goes through, most of the time near the middle of the second half of life. Often, the mechanism of development of arthrosis is caused by serious injuries in the form of fractures and damage to joints in people over 45 years of age.
Medical statistics say that osteoarthritis affects every third over 50 and every second over 70. In general, about 10% of the inhabitants of our planet suffer from arthrosis. Most of the time, osteoarthritis affects the knees and hip joints in the elderly. In addition, the joints of the fingers and ankle may be exposed to arthrosis.
The reasons for the development of diseases
It is clear that the causes of each disease are completely different.
For arthritis, they can be:
- Injuries of various origins, to a greater extent, recurrent and recurrent injuries associated with professional activities can cause the disease;
- Infections such as tuberculosis, fungal infection, SARS, influenza;
- Lack of vitamins and the resulting imbalance in metabolism;
- Body overload;
- Diseases of the nervous system;
- Malfunction of your own immune system;
- Have an inherited genetic tendency to arthritis.
Arthritis are frequent companions of people in professions such as seamstress, hairdresser, masseuse, loader, construction worker.
As for arthrosis, here the factors for the development of the disease are:
- Excess weight that affects the functioning of the joints;
- Malnutrition;
- Prolonged hypothermia;
- He suffered previously (perhaps until a long time ago) various types of injuries;
- Intoxication of the body;
- Metabolic diseases;
- Previous infectious diseases;
- Manifestations of autoimmune disorders;
- Perthes disease, manifested by alteration of the blood supply to the femoral head;
- Diseases of the thyroid gland;
Hereditary tendency to develop osteoarthritis, transmitted at the genetic level.
Annoying symptoms in arthritis
In arthritis, there is severe pain in the joints, especially when walking or performing other physical activity. The joint itself swells noticeably and the skin around the joint is warm to the touch. In addition, the skin may turn red. The patient develops a feeling of weakness, it is very difficult for him to make any movement with the affected arm or leg. It is especially difficult in the morning, after a night's rest. When pressing on the joint, the patient feels severe pain. When performing movements, the joints affected by arthritis can severely crack. The patient may have a high body temperature and the patient himself may have chills at this point. In acute arthritis, all symptoms appear simultaneously and abruptly. In chronic arthritis, symptoms slowly and gradually increase.
Arthrosis symptoms

With arthrosis, doctors distinguish four main symptoms of the disease:
- Pain in the joints.The pain is severe and acute. It begins the moment the movement begins and ceases with the transition to a state of rest. At night, the person practically does not feel pain and, having chosen a comfortable position, the patient can sleep in peace. The sensations of pain increase as the disease progresses. Pain is also worse in cold and rainy weather;
- Crushing joints.Due to the reduced freedom and smoothness of bone rotation, a strong cracking sound is heard in the joint. Experts distinguish arthritic crushing by a kind of "dry" sound. The more the disease develops, the stronger the crunch in the joints. A characteristic of compression in arthrosis is that compression is almost always accompanied by pain;
- Restriction of mobility of the joint itself.In arthrosis, in many cases, the limb is immobilized. This is due to the fact that bone growth occurs and the joint space narrows, which leads first to a limitation of mobility and then to a complete immobilization of the joint;
- Deformation of the joints.As a rule, this symptom is typical of the final stages of development of osteoarthritis, when osteophytes grow.
The difference between arthritis and arthrosis according to the clinical picture
It is quite clear that arthritis and arthrosis have different genesis as diseases. If arthritis is the result of a malfunction of the immune system or an infectious disease, then arthrosis refers more to diseases resulting from the body's aging processes. Thus, based on this, the clinical picture of the manifestations of arthritis and osteoarthritis will also be different.
Arthritis of the fingers
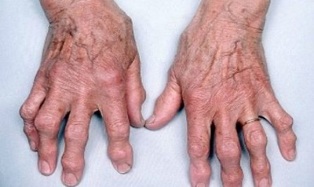
Thus, with arthritis of the fingers, the patient has severe pain that does not subside during rest and during rest. In addition, the skin around the affected joints turns red.
Arthritis can affect a different number of joints, from one (monoarthritis) to several (polyarthritis). The joints are swollen. The reaction when pressing on the joint can be acute pain.
As for the grinding at the joint, it may or may not be present.
Arthrosis of the fingers
It occurs more frequently in the elderly and, in women, arthrosis appears about 10 times more often than in strong sex. The main location is the joints between the phalanges of the fingers.
Any movement of the fingers causes uncomfortable pain in the patient. However, at rest, the pain is practically absent. The joints are swollen and there may be redness of the skin around the affected joint. Arthrosis is always accompanied by "dry" crushing of the joints.
The same picture is observed in cases of arthritis and osteoarthritis of the foot joints.
Treatment with chondroprotectors
In arthritis and osteoarthritis, cartilage is destroyed due to contact with the rough surface of the bone. As a result, the synovial fluid production process is interrupted, the cartilage is deprived of nutrition and the joint is deprived of the lubrication necessary for its normal functioning.
The chondroprotector prevents these pathological processes. The active substance in condoprotectors is glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate. The pharmaceutical forms of release of these substances are different and can be used by doctors depending on the situation.
Today, chondroprotectors are produced in the form:
- Solutions for injection;
- Tablets;
- Creams, ointments and gels.

Chondroprotective treatment should be started before complete cartilage collapse. Unfortunately, this treatment is absolutely useless when the cartilage is destroyed. The next thing to remember when treating with chondroprotectors is the duration of treatment. The fact is that the process of restoring cartilage is quite long and the minimum course of treatment should be six months, but practice shows that treatment with chondroprotectors takes an average of one and a half to two years. If the restoration is not completed, the destruction of the cartilage is resumed. As a rule, chondroprotectors have no side effects on the patient's body, the most that is observed in practice are mild intestinal disorders. The only complication may occur in the treatment of diabetic patients with chondroprotectants. When treating them, the insulin dose must be calculated correctly, as chondroprotectants contain glucose. It is also not recommended to use chondroprotectants during pregnancy, as well as for the treatment of children.
Today, in the arsenal of doctors who deal with the treatment of arthritis and arthrosis problems, there are a number of effective drugs for treatment.
Start treatment with chondroprotectors under the supervision of a doctor, otherwise the treatment may be ineffective.
Treatment with folk remedies
For arthritis, traditional medicine recommends several effective recipes:
- Apple cider vinegar.This substance is added to the water (1 teaspoon to a glass of water). The resulting solution is drunk before meals;
- Potato compress.Take green tubers for the compress.
Wash, cut into pieces without peeling. The potatoes are heated in water to a temperature of 38 degrees. Then, a compress is applied to the painful area. The potato layer should be 1, 5 - 2 centimeters. You must bet at night. The course of treatment in this way is seven to ten days.
Ointments in the treatment of arthritis and osteoarthritis
In the early stages of the development of arthritis, as well as osteoarthritis, the use of ointments for external use can help in the treatment of the patient. A specialist will select the appropriate medication based on the results of the exam.

























